Aspscr1 gene 243393-Aspscr1 gene
ASPSCR1 tether for SLC2, UBX domain containing Aliases TUG, ASPL, ASPS, RCC17, UBXD9, UBXN9, ASPCR1 Location 17q253 Summary The protein encoded by this gene contains a UBX domain and interacts with glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) This protein is a tether, which sequesters the GLUT4 in intracellular vesicles in muscleASPSCR1 expression was also found in all cancer cell lines tested Independently, Heimann et al (01) identified the ASPSCR1 gene, which they called RCC17, partnered with TF in two 5yearold Belgian girls of African origin in whom papillary renal cell carcinomas () carried the translocation t(X;17)(p112;q25)By conditionally expressing in mice the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), we generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile, enabling study of the conditions supportive of tumor development Mouse tumors demonstrated angiogenic gene expression in the frank absence of hypoxia and were

Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Abstract Europe Pmc
Aspscr1 gene
Aspscr1 gene-Symbol Description Category GIFtS GC id Score;Type protein_coding_gene Location Chr 11 Mapping Details/Browsers Description Human ortholog(s) of this gene implicated in alveolar soft part sarcoma




Nsfl1c Gene Genecards Nsf1c Protein Nsf1c Antibody
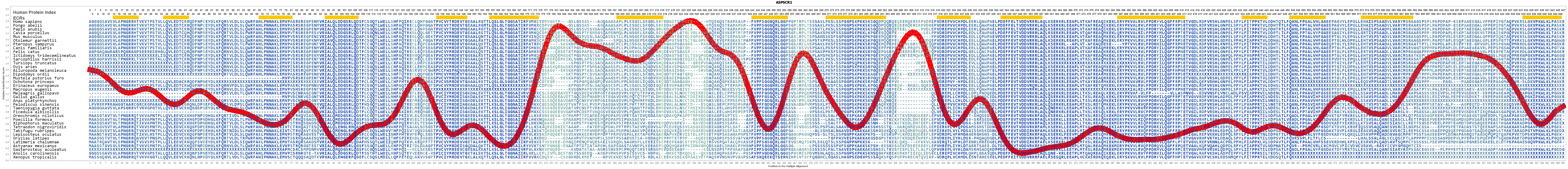
The gene view histogram is a graphical view of mutations across ASPSCR1 These mutations are displayed at the amino acid level across the full length of the gene by default Restrict the view to a region of the gene by dragging across the histogram to highlight the region of interest, or by using the sliders in the filters panel to the leftTaxonomy i Protein names i Submitted name Tethercontaining UBX domain for GLUT4 Imported Aspscr1 Tug 550 Annotation score F6S7C9 F6S7C9_MOUSEAlveolar soft part sarcoma is characterized by a der(17)(X;17)(p112;q25) translocation resulting in an ASPSCR1TF gene fusion, the distinctive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma subset harbors a t(X;11)(p112;q13) translocation resulting in a YAP1TF gene
Gene fusions were detected in 905% (57/63) cases, of which 947% (54/57) cases showed relatively more common gene fusions, including SFPQTF (n = 15), ASPSCR1TF (n = 13), NONOTF (n = 8View mouse Aspscr1 Chr with phenotypes, sequences, polymorphisms, proteins, references, function, expressionAlveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare malignancy that, since its initial description, remains a neoplasm of uncertain histogenesis The disease‐defining molecular event characterizing the diagnosis of ASPS is the ASPSCR1‐TF fusion gene Following identification of an index case of ASPS with a novel TF fusion partner, we performed a retrospective review to
Description Homo sapiens ASPSCR1 tether for SLC2, UBX domain containing (ASPSCR1), transcript variant 2, mRNA (from RefSeq NM_) RefSeq Summary (NM_) The protein encoded by this gene contains a UBX domain and interacts with glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) This protein is a tether, which sequesters the GLUT4 in intracellular vesicles in muscleHUMAN PROTEIN ATLAS SUMMARYi General description of the gene and the encoded protein (s) using information from HGNC and Ensembl, as well as predictions made by the Human Protein Atlas project Proteini Full gene name according to HGNC ASPSCR1, UBX domain containing tether for SLC2 Gene nameiOther interactions of ASPSCR1 The der (17)t (X;17) (p11;q25) of human alveolar soft part sarcoma fuses the TF transcription factor gene to ASPL, a novel gene at 17q25 8 The status of the TP53 alleles was followed at different stages by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and allelespecific PCR ( ASPCR) on total DNA, as well as flow




Anti Aspscr1 Antibody Hpa Atlas Antibodies




Genetic Diversity In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma A Subset Contain Variant Fusion Genes Highlighting Broader Molecular Kinship With Other Mit Family Tumors Dickson Genes Chromosomes And Cancer Wiley Online Library
A conditional expression in mice of the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile ASPL is a cofactor of31 ASPSCR1 Silencer Select Predesigned, Validated, and Custom siRNA in Standard, HPLC, and Invivo Ready PuritiesGene Fusions Fusion Partners Original Annotation ASPSCR1TF 31 ASPSCR1TF ASPSCR1TF alveolar soft part sarcoma Pubmed 17 ASPSCR1TF ASPSCR1TF Adenocarcinoma, Alveolar soft part sarcoma, renal cell carcinoma




Polyclonal Glut4 Antibody Mybiosource




The T X 17 P11 25 Translocation A The Aspscr 1 Gene Is Located At Download Scientific Diagram
OncoKB is a precision oncology knowledge base developed at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center that contains biological and clinical information about genomic alterations in cancerGene Aspscr1 Organism Mus musculus (Mouse) Status UnreviewedAnnotation score Experimental evidence at protein level i Names &Alveolar soft part sarcoma with ASPSCR1 TF fusion Cytogenetics der (X)t (X;17) (p11;q25) is consistently involved;




Aspscr1 Antibody N Term 102 130
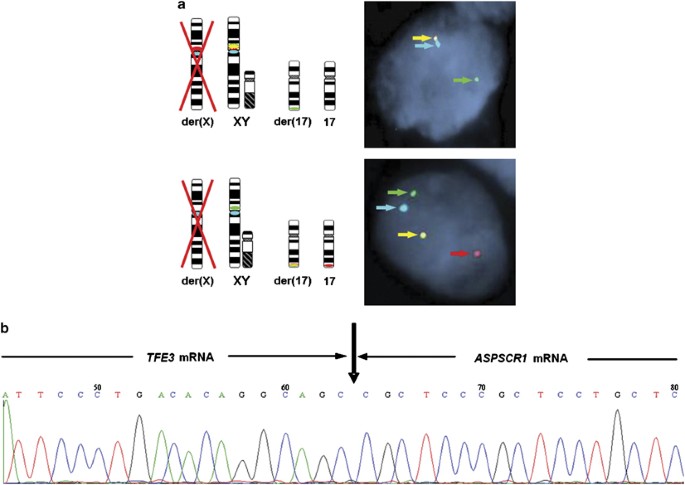



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology
Tethering protein that sequesters GLUT4containing vesicles in the cytoplasm in the absence of insulin Modulates the amount of GLUT4 that is available at the cell surface (By similarity) Enhances VCP methylation catalyzed by VCPKMT The protein encoded by this gene contains a UBX domain and interacts with glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) This protein is a tether, which sequestersAspscr1 Q9BZE9 Transcriptional coactivator stimulating NR5A1 andliganddependent NR1H3/LXRA and PPARG transcriptional activitiesEnhances the DNAbinding activity of ATF1, ATF2, CREB1 and NR5A1Regulates nitric oxid synthase activity probably by sequesteringcalmodulin in the cytoplasmXp11 translocation renal cell carcinomas harbor chromosome translocations involving the Xp11 breakpoint, resulting in gene fusions involving the TF gene The most common subtypes are the ASPSCR1



Cell Com



Psammoma Bodies
Phenotype data for mouse gene Aspscr1 Discover Aspscr1's significant phenotypes, expression, images, histopathology and more Data for gene Aspscr1 is all freely available for downloadIt implicates 1 the formation of a hybrid gene at the breakpoint, and also, 2 gain in Xp11pter sequences, and loss of heterozygocity in 11q25qter, with possible implications Hybrid/Mutated GeneThe ASPSCR1 fusion gene–expressing ex vivo model defines tumorigenic activity of the Cterminal domains in TFE/MITF family proteins TF belongs to the TFE/MITF transcription protein family, which has been found to be involved in human cancer and within which the DNA binding bHLH leucine zipper motif is well conserved




Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Translocation Fish Probe Kit Cytotest




Aspscr1 Promotes Methylation Of Vcp By Mettl21d A In Vitro Download Scientific Diagram
Context PubMed ASPSCR1 Title/Abstract AND TF Title/Abstract AND fusion Title/Abstract Functional or gene categories assigned by FusionGDB annotation Oncogene involved fusion gene, inframe and retained their domain * DoF score (Degree of Frequency) = # partners X # break points X # cancer typesThe TF fusion partners in the latter three neoplasms have been fairly consistent;Differential expression of cathepsin K in neoplasms harboring TF gene fusions Modern Pathology, 11 Diego Segala Stefano Gobbo 9 More Download PDF Download Full PDF Package This paper A short summary of this paper 36 Full PDFs related to this paper




Molecular Landscape In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Implications For Molecular Targeted Therapy Sciencedirect




Integrative Clinical And Molecular Characterization Of Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Biorxiv
The mission of the Public Health Genomics is to integrate advances in human genetics into public health research, policy, and programsGene names and symbols associated with ASPSCR1 ASPSCR1, UBX domain containing tether for SLC2 (ASPSCR1) antibody alveolar soft part sarcoma chromosome region, candidate 1 S homeolog (aspscr1S) antibodyAspscr1 Gene Name alveolar soft part sarcoma chromosome region, candidate 1 (human) Gene Aliases K01Rik, ASPC, ASPCR1, ASPL, ASPS, RCC17, TUG Chromosome Location Chr11 on Build GRCm38 UniGene ID Mm2940 Species Mouse Species Specific ID (Flybase ID)




Lsp Aspscr1 5 Fish Probe Cytotest




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Kobos 13 The Journal Of Pathology Wiley Online Library
Up to12%cash backAlveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare soft tissue sarcoma characterized by an alveolar or organoid arrangement of polygonal tumour cells separated by fibrovascular septa A specific fusion gene ASPS critical region 1 (ASPSCR1)—TF was detected in ASPS Despite being a slowgrowing tumour without pain and dysfunction, ASPS isIn addition to wildtype TF, ASPSCR1TF fusion transcripts (three type 1 and two type 2 transcripts) were detected in all cases Conclusions Molecular confirmation of ASPSCR1TF gene fusion is applicable to routinely processed archival and diagnostic tumour samples and aids in the differential diagnosis of ASPSASPSCR1 (ASPSCR1 Tether For SLC2, UBX Domain Containing) is a Protein Coding gene Diseases associated with ASPSCR1 include Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma, Xp11AssociatedAmong its related pathways are Vesiclemediated transport and Translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membraneAn important paralog of this gene is UBXN6



1



Plos One Using Regulatory And Epistatic Networks To Extend The Findings Of A Genome Scan Identifying The Gene Drivers Of Pigmentation In Merino Sheep
Translocation t (X;17) (p11;q25) with TF forms a ASPSCR1TF fusion protein 1 Publication Manual assertion based on experiment in i Ref1 The der (17)t (X;17) (p11;q25) of human alveolar soft part sarcoma fuses the TF transcription factor gene to ASPL, aOncogenic rearrangements of the TF transcription factor gene are found in two distinct human cancers These include ASPSCR1–TF in all cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) and ASPSCR1–TF, PRCCTF, SFPQTF and others in a subset of paediatric and adult RCCs Here we examined the functional properties of the ASPSCR1–TFThis results in a fusion of the transcription factor (TF) gene located at Xp11 with the ASPS chromosome region, candidate 1 gene at 17q25 (ASPSCR1, or ASPL), creating the ASPSCR1TF translocation , ASPSCR1TF is the driving oncogenic
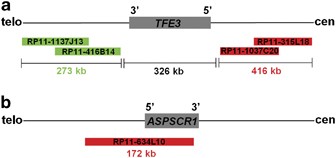



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




Ubxn2a Gene Genecards Ubx2a Protein Ubx2a Antibody
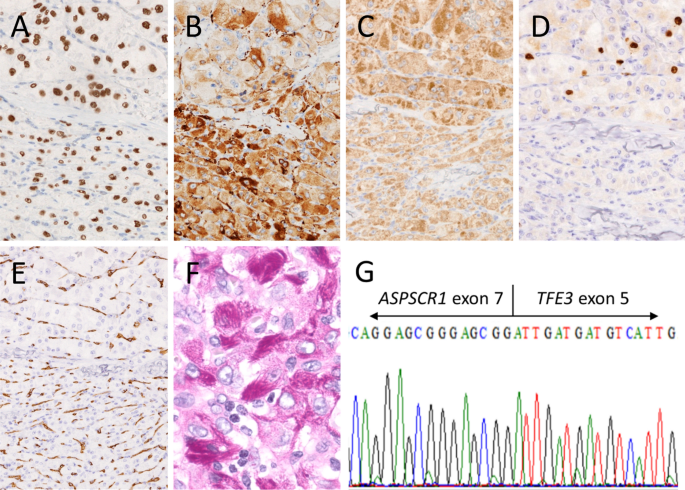
Different gene fusions were identified in 5 neoplasms One case had a FUSCREM gene fusion 6, 9, two cases had SS18 SSX gene fusions characterizing SS, and another two cases had TFASPSCR1 gene fusions characterizing ASPS (for details, see Table 1) Comparison of referral opinion/diagnosis and final diagnosisFunctional Associations ASPSCR1 has 4,6 functional associations with biological entities spanning 8 categories (molecular profile, organism, chemical, functional term, phrase or reference, disease, phenotype or trait, structural feature, cell line, cell type or tissue, gene, protein or microRNA) extracted from 77 datasetsDetection of the ASPSCR1TF fusion transcript and TF Immunohistochemistry The molecular signature of ASPS is a specific der(17)t(X;17)(p112;q25), which results in the fusion of either exon 6 (type 1) or exon 5 (type 2) of the TF transcription factor gene (Xp11) with ASPSCR1 (17q25), usually in a nonbalanced manner although reciprocal translocations have



Plos One Gene Expression Profiling Of Lymphoblasts From Autistic And Nonaffected Sib Pairs Altered Pathways In Neuronal Development And Steroid Biosynthesis
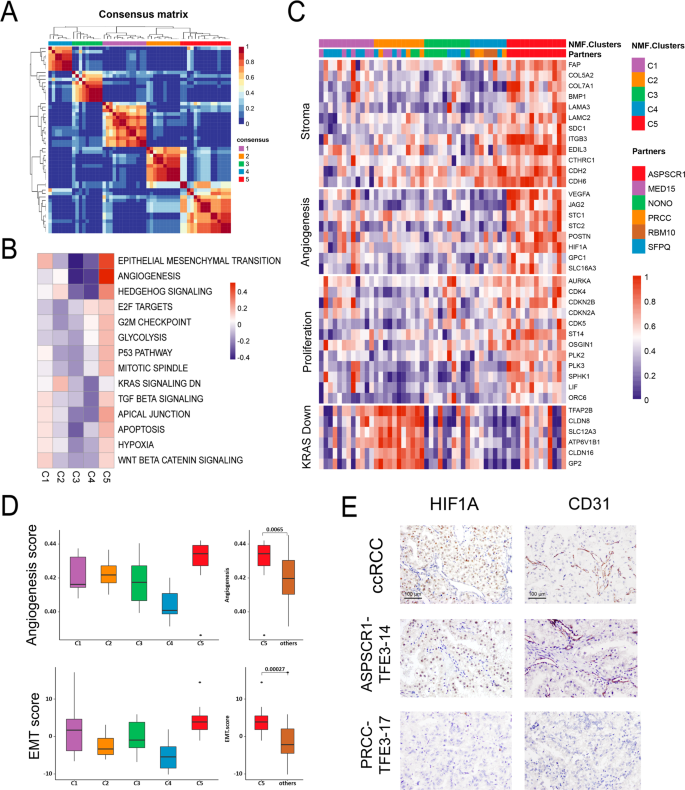



Integrated Exome And Rna Sequencing Of Tfe3 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Nature Communications
Heimann et al (01) identified the ASPSCR1 gene, which they called RCC17, partnered with TF in two 5yearold Belgian girls of African origin in whom papillary renal cell carcinomas carried the translocation t(X;17)(p112;q25)1 ASPSCR1 ASPSCR1 Tether For SLC2, UBX Domain Containing Protein Coding 41 GC17P 47 2 TF Transcription Factor Binding To IGHM Enhancer 3The ASPSCR1TF gene fusion is the same gene fusion found in alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), a rare pediatric neoplasm of uncertain histogenesis However, the translocation in Xp11 translocation RCC is balanced, which may contribute to the differences seen at the clinical and histopathologic levels between Xp11 translocation RCC and ASPS




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Abstract Europe Pmc




Figure 1 Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies
Translocation t(X;17)(p11;q25) of this gene with transcription factor TF gene results in a ASPSCR1TF fusion protein in alveolar soft part sarcoma and in renal cell carcinomas Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found Chemical Modification DNA/RNA Length 80 nt Affinity (Kd) 1nM~1μM Binding Conditions/BufferOncogenic rearrangements of the TF transcription factor gene are found in two distinct human cancers These include ASPSCR1TF in all cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) and ASPSCR1TF, PRCCTF, SFPQTF and others in a subset of paediatric and adult RCCs Here we examined the functiGENERAL INFORMATIONi General description of the gene and the encoded protein (s) using information from HGNC and Ensembl, as well as predictions made by the Human Protein Atlas project Gene namei Official gene symbol, which is typically a short form of the gene name, according to HGNC ASPSCR1
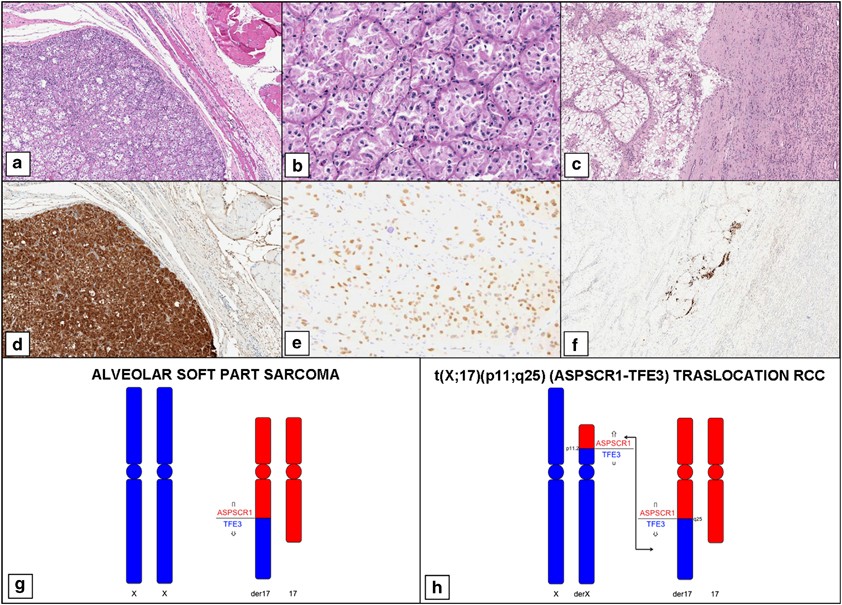



Differential Expression Of Cathepsin K In Neoplasms Harboring Tfe3 Gene Fusions Modern Pathology




Aspl Tfe3 Oncoprotein Regulates Cell Cycle Progression And Induces Cellular Senescence By Up Regulating P21 Sciencedirect
ZDBGENE Name ASPSCR1 tether for SLC2, UBX domain containing Symbol aspscr1 Nomenclature History Previous Names zgc;ASPSCR1 Name ASPSCR1 tether for SLC2, UBX domain containing Synonyms NCBI Gene IDs Homo sapiens 638 Mus musculus Gallus gallusDisease ASPSCR1/TF renal cell carcinomas harbor the same gene fusion as alveolar soft part sarcoma, but belong to the family of Xp11 translocation RCC Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma (RCCs) harbor gene fusions involving TF transcription factor The The t (6;11) RCCs harbor a specific MALAT1 (Alpha) TFEB gene fusion



Documents Irevues Inist Fr



Aspscr1 Wikipedia
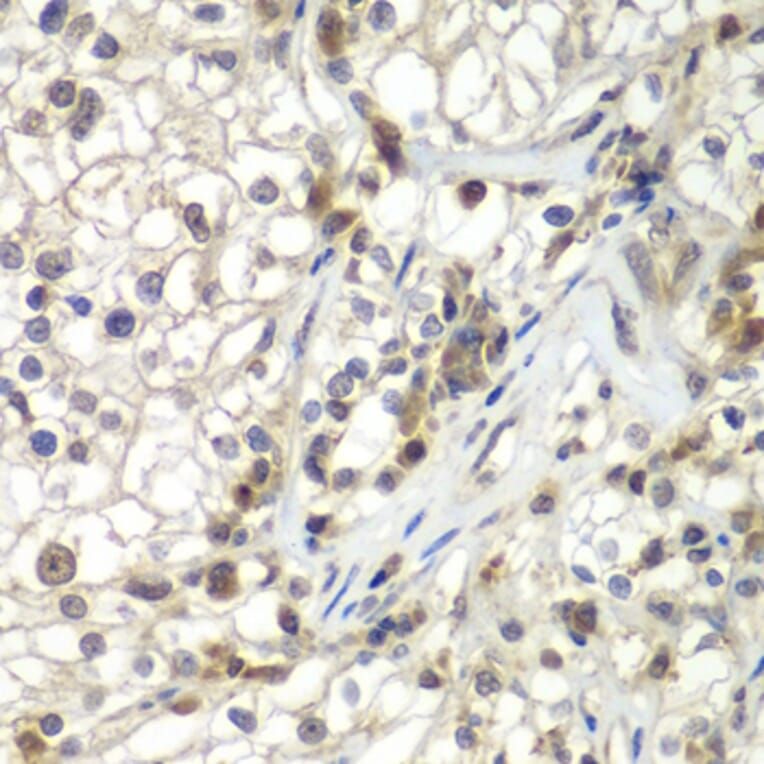
The exact same chromosomal changes are found in a rare form of kidney cancer, ASPSCR1TF translocation renal cell carcinoma in which the chromosomal translocation is "balanced" as opposed to the "unbalanced" translocation seen in ASPS This is a cancer of an entirely different nature Researchers are unsure why the ASPSCR1TF gene fusion causes ASPS in some people and aASPSCR1 (arrow) was detected using the purified antibody ASPSCR1 Antibody flow cytometry of HeLa cells (right histogram) compared to a negative control cell (left histogram) FITCconjugated goatantirabbit secondary antibodies were used for the analysisASPSCR1 gene product ASPL, ASPS, TUG, UBXD9, UBXN9 The protein encoded by this gene contains a UBX domain and interacts with glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) This protein is a tether, which sequesters the GLUT4 in intracellular vesicles in muscle and fat cells in the absence of insulin, and redistributes the GLUT4 to the plasma membrane




Nsfl1c Gene Genecards Nsf1c Protein Nsf1c Antibody



Abubaker Elshaikh Neck Mass Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Positive Tfe3 Aspscr1 Gene Rearrangement Cytology Surgpath



Tfe3 Transcription Factor



Pathology Jhu Edu




Activity And Safety Of Crizotinib In Patients With Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma With Rearrangement Of Tfe3 European Organization For Research And Treatment Of Cancer Eortc Phase Ii Trial Create Annals
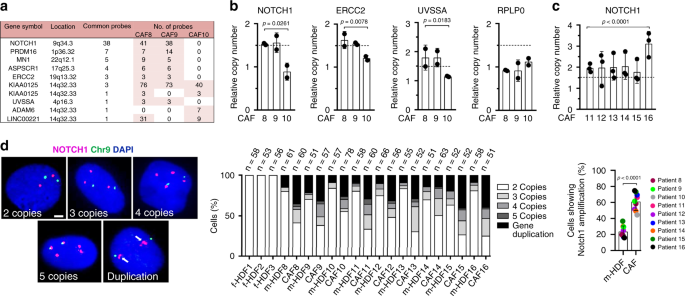



Notch1 Gene Amplification Promotes Expansion Of Cancer Associated Fibroblast Populations In Human Skin Nature Communications



Cancerres crjournals Org




The Fusion Oncogene Aspscr1 Tfe3 Directs Epigenetic Induced Autophagy In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Barrott 19 The Faseb Journal Wiley Online Library




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of The Bladder With Aspscr1 Tfe3 Gene Fusion As A Secondary Malignancy Sciencedirect




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table
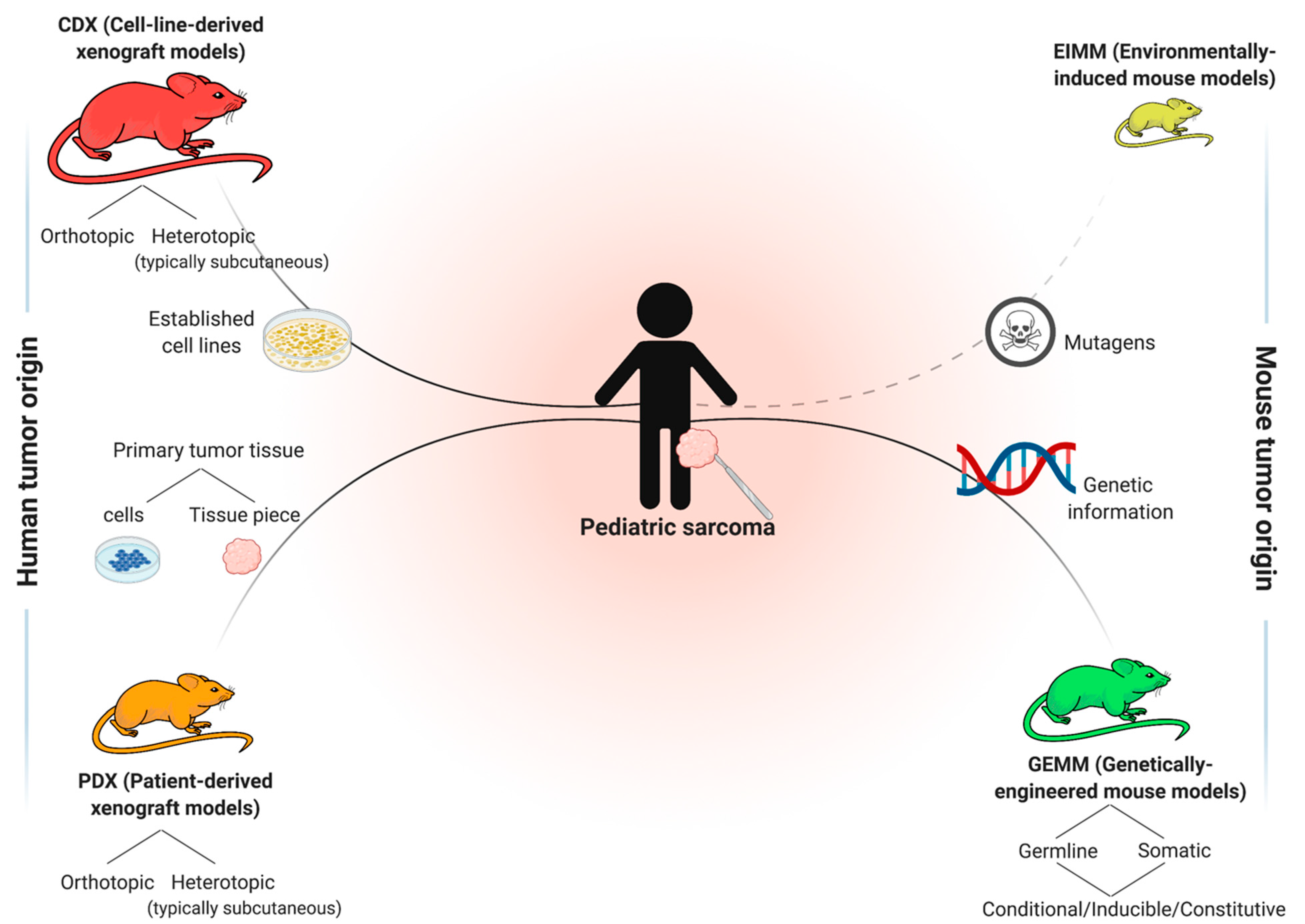



Jcm Free Full Text Preclinical In Vivo Modeling Of Pediatric Sarcoma Promises And Limitations Html



Aspscr1 Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Critical Region 1




Anti Aspcr1 Antibody Products Biocompare




Dera Gene Genecards Deoc Protein Deoc Antibody




Aspscr1 Protein Pan Troglodytes String Interaction Network




Figure 2 From Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Semantic Scholar




The T X 17 P11 25 Translocation A The Aspscr 1 Gene Is Located At Download Scientific Diagram




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Unveils Novel Mechanisms Of Metastasis Cancer Research




Figure 5 From Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Asps Semantic Scholar



Zfin Gene Aspscr1
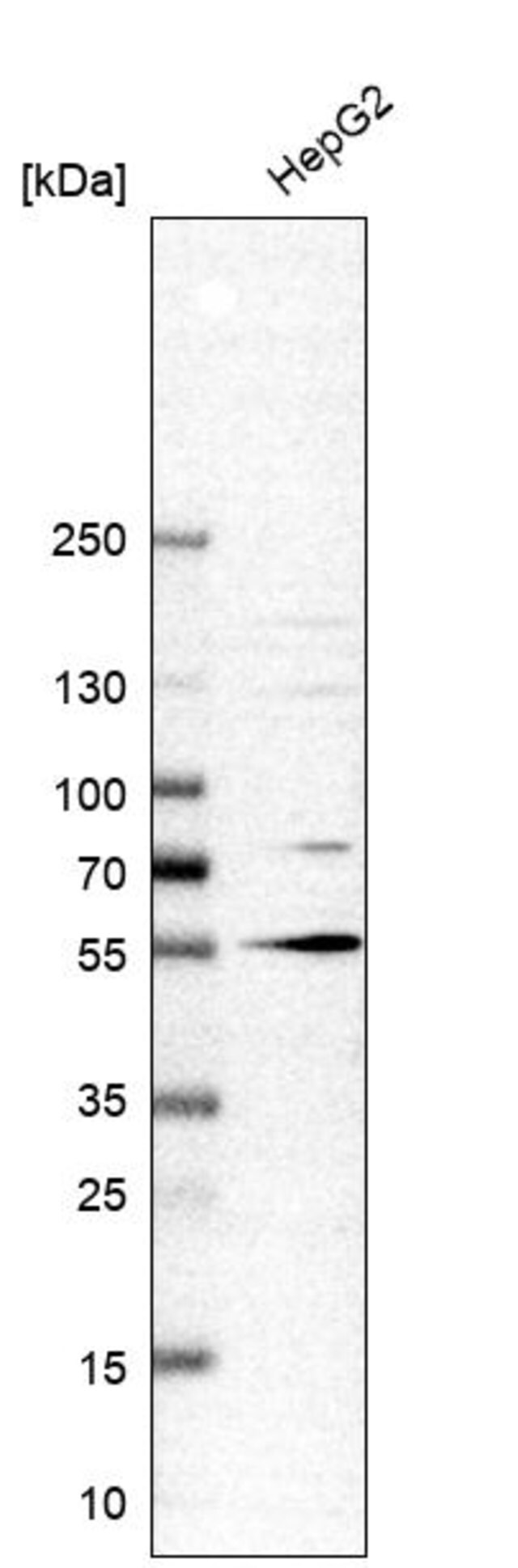



Anti Aspscr1 Antibody Produced In Rabbit Prestige Antibodies Powered By Atlas Antibodies Affinity Isolated Antibody Buffered Aqueous Glycerol Solution



Cytoscape App Store Jepetto
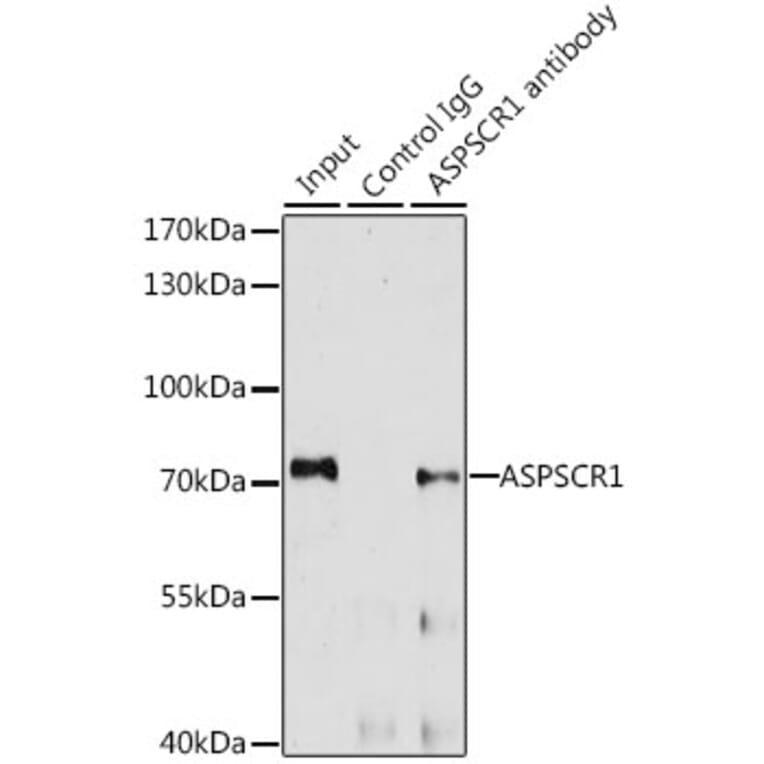



Anti Aspscr1 Antibody A Antibodies Com




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of The Bladder With Aspscr1 Tfe3 Gene Fusion As A Secondary Malignancy Sciencedirect
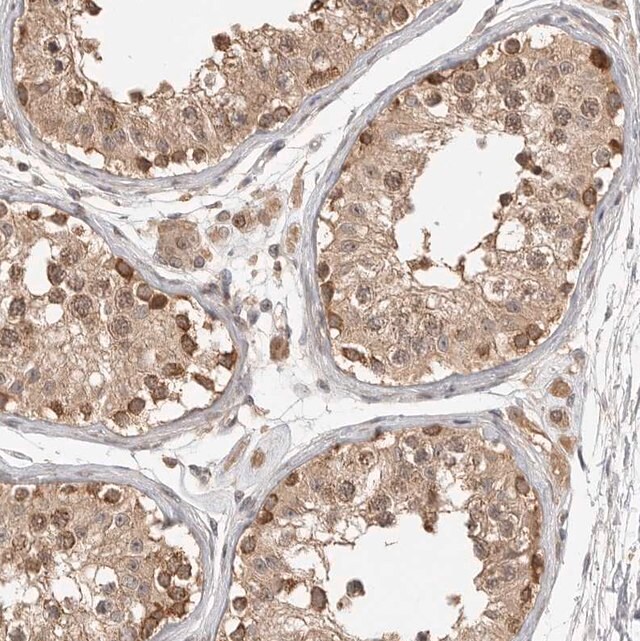



Anti Aspscr1 Antibody Produced In Rabbit Prestige Antibodies Powered By Atlas Antibodies Affinity Isolated Antibody Buffered Aqueous Glycerol Solution




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomagenesis In The Mouse A Role For Lactate In The Tumor Microenvironment Sciencedirect




Positive Tumor Response To Combined Checkpoint Inhibitors In A Patient With Refractory Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma A Case Report Jco Global Oncology




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies




Gene Of The Month Tfe 3 Journal Of Clinical Pathology




Gene Of The Month Tfe 3 Journal Of Clinical Pathology




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies



Cytotest Com




Genomics Morphoproteomics And Treatment Patterns Of Patients With Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma And Response To Multiple Experimental Therapies Molecular Cancer Therapeutics




Shkbp1 Gene Genecards Shkb1 Protein Shkb1 Antibody



Aspscr1 Gene Genecards Aspc1 Protein Aspc1 Antibody



Anti Aspscr1 Antibody A Antibodies Com



Abubaker Elshaikh Neck Mass Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Positive Tfe3 Aspscr1 Gene Rearrangement Cytology Surgpath



Xp11 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma




Rt Pcr Findings Identification Of The Aspscr1 Aspl Tfe3 Fusion Download Scientific Diagram



Primary Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of Cheek Report Of A Case And Review Of The Literature Springerlink



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3




Genetic Diversity In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma A Subset Contain Variant Fusion Genes Highlighting Broader Molecular Kinship With Other Mit Family Tumors Dickson Genes Chromosomes And Cancer Wiley Online Library




Hsalng Gene Genecards Hsalng Rna Gene



Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Translocation Fish Probe Kit 10 Tests Diagnostic Technology




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Abstract Europe Pmc



1




Mit Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Semantic Scholar




Aspscr1 Antibody N Term 102 130




Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Abstract Europe Pmc



Cell Com




X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Scientific Diagram



Aspscr1 Mgi Mouse Gene Detail Mgi Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Chromosome Region Candidate 1 Human
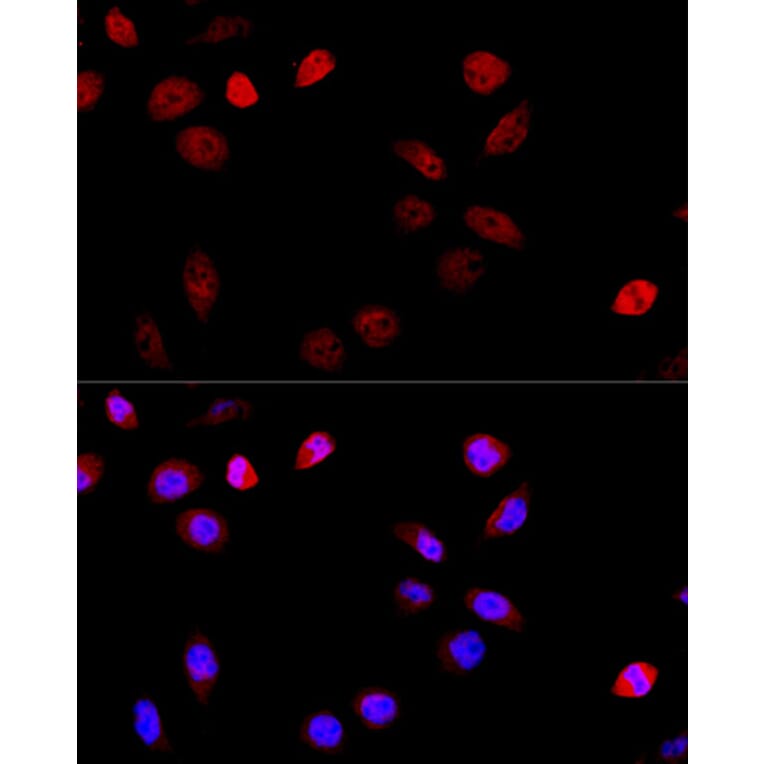



Anti Aspscr1 Antibody A Antibodies Com
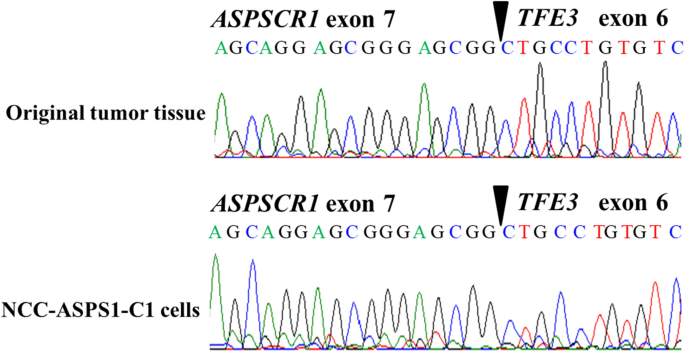



Establishment And Characterization Of Ncc Asps1 C1 A Novel Patient Derived Cell Line Of Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Springerlink




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies




Tug Aspscr1 Rabbit Pab Polyclonal Antibodies Abclonal




Ubxd9 Aspl Aspcr1 Aspscr1 Ubxd9 Aspl Aspcr1 Aspscr1 Kits Biocompare



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3




Aspscr1 Gene Genecards Aspc1 Protein Aspc1 Antibody



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3
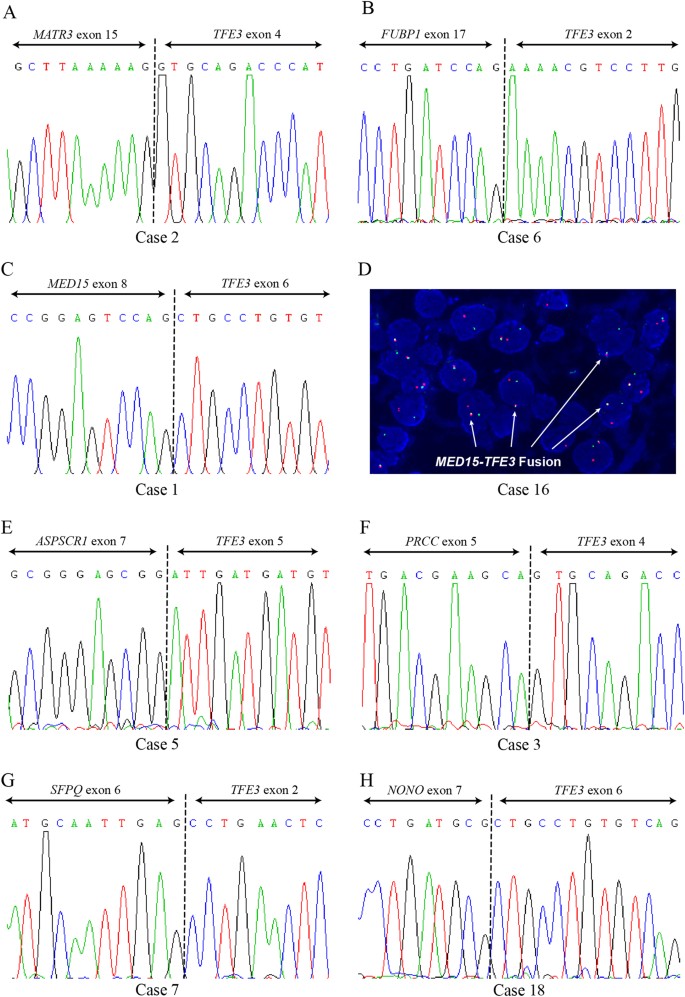



Rna Sequencing Of Xp11 Translocation Associated Cancers Reveals Novel Gene Fusions And Distinctive Clinicopathologic Correlations Modern Pathology




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Abstract Europe Pmc



A Newly Uncovered Group Of Distantly Related Lysine Methyltransferases Preferentially Interact With Molecular Chaperones To Regulate Their Activity




Abstract B The Molecular Function Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Clinical Cancer Research



Aspscr1 Human




Ubxd9 Aspl Aspcr1 Aspscr1 Ubxd9 Aspl Aspcr1 Aspscr1 Kits Biocompare




Nsfl1c Protein Human String Interaction Network
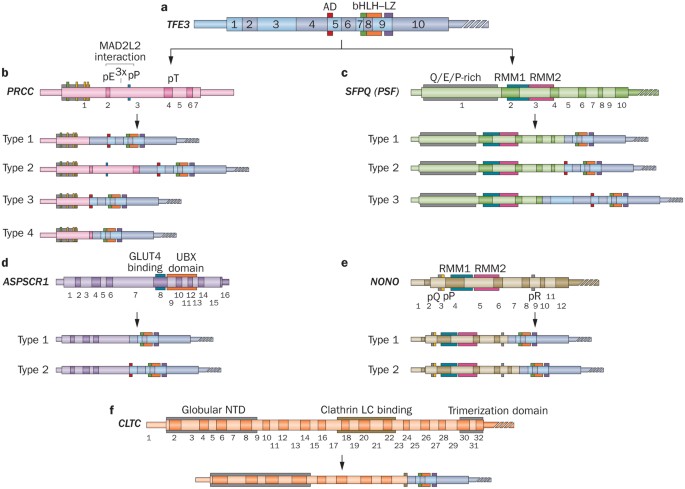



Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Nature Reviews Urology



Aspscr1 1 553 His Human Protein Ar509pu S Origene




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Unveils Novel Mechanisms Of Metastasis Cancer Research



Abubaker Elshaikh Neck Mass Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Positive Tfe3 Aspscr1 Gene Rearrangement Cytology Surgpath




Molecular Landscape In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Implications For Molecular Targeted Therapy Sciencedirect




Signaling Schematic For Asps Tumors And Novel Therapeutic Targets A Download Scientific Diagram




Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Abstract Europe Pmc



Cell Com
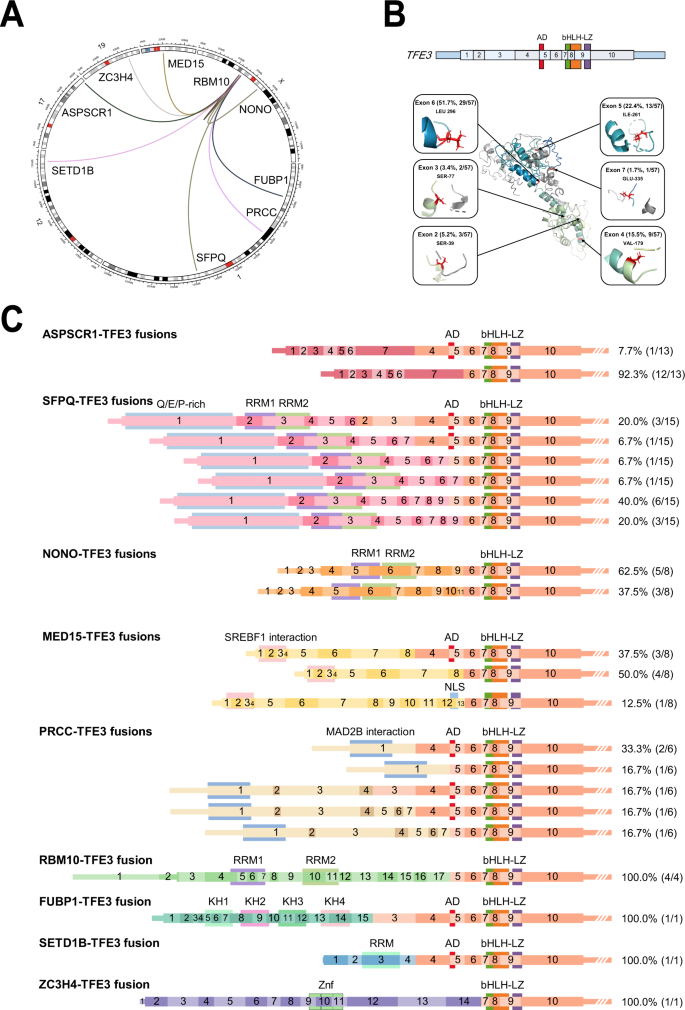



Integrated Exome And Rna Sequencing Of Tfe3 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Nature Communications




Aspscr1 Protein Expression Summary The Human Protein Atlas



Aspscr1 Aspscr1 Tether For Slc2a4 Ubx Domain Containing Gene Report Biogps
コメント
コメントを投稿